When Naresh Bhai experienced chest pain for the first time, he did not expect it to point towards something as serious as a heart disease. Naresh was just 43 years when he was diagnosed with the single-vessel disease or what most people know as coronary heart disease – a condition wherein the arteries are narrowed or blocked due to fat deposition and fail to supply blood to the heart muscles.
In recent years, coronary heart diseases are becoming more and more common among the younger population. Scientific studies, in the last few years, have made some shocking revelations about the incidence of coronary disorders in India. Indians develop heart disease earlier by 5-10 years compared to other ethnic populations, says one study. Another study reports that in India, 52% of the deaths before age 70 occur due to heart diseases and stroke.
The risk factors mainly include high blood cholesterol levels, sedentary lifestyle, family history, gender, genetics, age, etc. Coronary heart diseases are never to be ignored, as these can lead to heart attacks, coronary artery spasm or congestive heart failures, which can be fatal.
In Naresh’s case, there was no family history or comorbidities, such as diabetes or high blood pressure that are usually associated with heart diseases. However, he was an occasional tobacco chewer.
Naresh presented himself at HCG Hospitals, Bhavnagar with chest pain, and his diagnostic reports suggested critical single-vessel disease in the left anterior descending artery, whose function is to supply blood to crucial parts of the heart.
Before visiting HCG, PTCA (Percutaneous Transluminal Coronary Angioplasty) along with stenting, which is considered to be the gold standard for the treatment of single-vessel disease, was scheduled for him. PTCA is a minimally invasive procedure to open up blocked coronary arteries and facilitate optimal blood supply to the heart. However, it had to be abandoned due to an unexpected LAD dissection. This complication ruled out stenting for Naresh.
He was further referred to HCG for Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG), which is the traditional open-heart surgery performed to treat CAD. However, the multidisciplinary team at HCG recommended a simpler, yet equally effective treatment of MIDCAB or minimally invasive direct coronary artery bypass. Considering the patient’s young age, the team decided that it would be ideal to go with a procedure that helped him get back to his normal life as early as possible.
MIDCAB is usually recommended for single-vessel disease – especially when it is not possible to insert a stent. CABG, on the other hand, is more effective when there are more than two vessels damaged.
After explaining the procedure, its risks and possible after-effects to the patient and his family members, the expert team, headed by Dr Brij Mohan Singh, scheduled MIDCAB surgery for Naresh.
The surgery was successful. The recovery was quick too – Naresh was discharged just two days after his surgery.
LAD dissection is one of the uncommon complications of stenting – however, it is not rare. In these cases, doctors traditionally went for open-heart surgeries which have their own set of advantages and disadvantages. Open heart surgeries are ideal for more complicated coronary disorders.
Some of the major shortcomings of open-heart surgeries include excessive blood loss, prolonged healing periods due to bone cuts, extended hospital stay, temporary breathing difficulties, etc.
These complications, which could have been avoided if a simpler procedure was used, could become a burden physically and financially for the patients and also affect their quality of life. Minimally invasive surgeries, on the other hand, come with fewer complications.
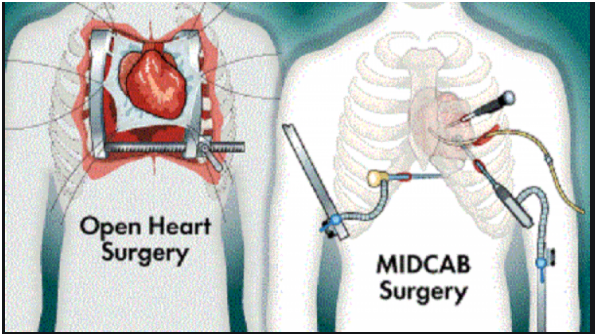
MIDCAB is also known as keyhole surgery, since this surgery involves tiny incisions, called thoracotomies, instead of one large incision. During the procedure, a keyhole opening is made on the left side of the chest, between the ribs, to access the heart. While the heart is still beating, the bypass is precisely grafted with the help of endoscopic stabilization devices without interfering with the functioning of the heart.
HCG has always been at the forefront in introducing groundbreaking technologies and patient-centric treatment techniques in India.Our latest introduction of MIDCAB programme at Bhavnagar, Gujarat, just like our other programmes in the past, is all set to help the patients in this region with safe and effective treatment plans.
At HCG, each case is carefully studied by a large group of specialists before devising the treatment plan. This is because we give equal importance to both the life and the quality of life of every patient we treat.