Introduction
The decline of cognitive functions involving memory, reasoning, and behaviour characterises Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
Families go through difficult times when taking care of such patients who experience a decrease in their ability to reason, remember things, and act normal as this condition becomes more demanding across all aspects of life.
With the increasing ageing population worldwide, Alzheimer’s is slowly becoming an epidemic that needs immediate attention.
It is approximated at a global scale that there are more than fifty million cases of dementia, with around 60–70% being accounted for by Alzheimer's disease.
Understanding Alzheimer Disease
What is Alzheimer's Disease?
Alzheimer's disease is the leading cause of dementia, which results in progressive loss of thinking capacity, behavioural conduct, and social skills.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact Alzheimer's causes are still unknown, although there are some identified risk factors for this disease. These include:
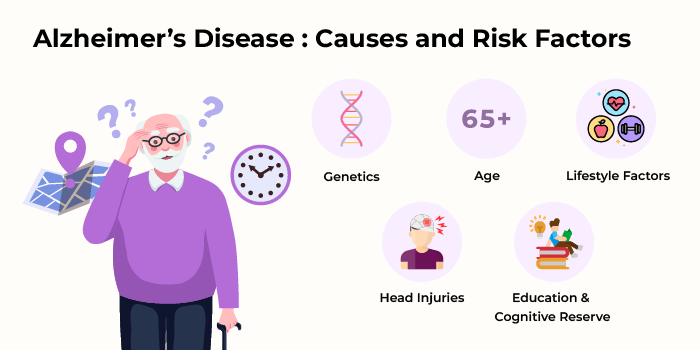
Genetics: Having immediate family members who have Alzheimer’s increases one’s chances of getting the disease more than if this history were absent. Certain genes, like the APOE-e4gene, can increase the risk of developing AD.
Age: The most common Alzheimer's risk factor is advancing age. The majority of individuals diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease are elderly.
Lifestyle Factors: Cardiovascular health matters a lot. Hypertension, high cholesterol, diabetes, obesity, and lack of exercise may contribute to brain health degeneration.
Head Injuries: A significant head trauma in the past may predispose one to Alzheimer’s in old age.
Education & Cognitive Reserve: Research has indicated that higher education levels may be protective against the disease. Also, mental activities such as reading and puzzles may create some form of “cognitive reserve” that helps guard against Alzheimer’s disease.
Diagnostic Process
Early Signs and Symptoms
Detecting Alzheimer’s at its early stage is important to maximise treatment effects. However, these signs may sometimes appear mild and be mistaken for normal ageing. Some of the first Alzheimer's symptoms are as follows:
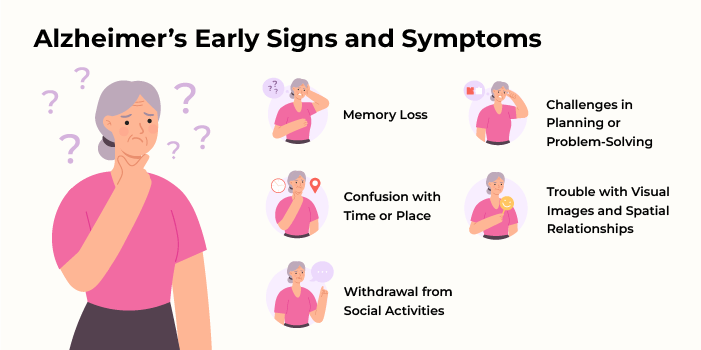
Memory Loss: Inability to remember what has been read or seen, including important dates and events.
Challenges in Planning or Problem-Solving: Trouble following through complex plans, keeping track of them, or doing simple calculations.
Confusion with Time or Place: Problems remembering when particular events should occur or losing way in places they know well.
Trouble with Visual Images and Spatial Relationships: Failure to comprehend visual cues like those found in pictures and artwork; thus, posing risks on one’s side such as imbalance, failure to read well, and misjudging distances.
Withdrawal from Social Activities: Failure to maintain normal social contacts or abandoning customary pursuits.
Diagnostic Procedures
For Alzheimer's diagnosis, a combination of physical examination, patient history, and imaging techniques are employed:
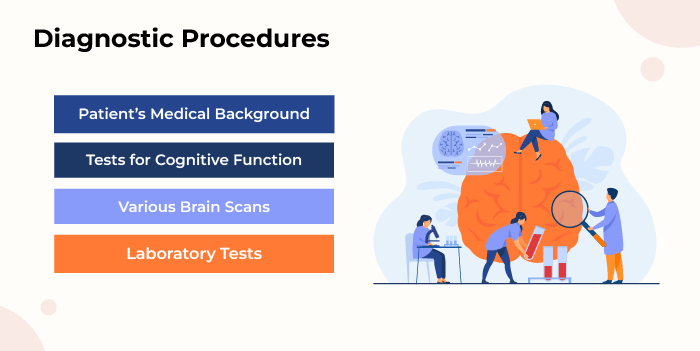
Patient’s Medical Background: This encompasses a detailed examination of the patient’s general well-being, lifestyle, and family tree. In most cases, doctors talk to close relatives to get a clear picture of the patient’s behaviour or thought process changes.
Tests for Cognitive Function: Cognitive function is assessed using memory tests such as the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE). For example, patients might have to recall a list of words, draw a clock, or perform some easy calculations.
Various Brain Scans: Imaging tests, like MRI and PET scans, aid in studying the structure and changes of the human brain related to this disorder, like shrinkages in certain areas and amyloid plaque accumulation.
Laboratory Tests: Blood analysis is performed to eliminate differential diagnoses of cognitive disorders that may be related to vitamin deficiencies, infections, or thyroid problems, among others.
Treatment Approaches by Hubli Neurological Specialists
HCG Suchirayu Hospital has some of the most highly experienced neurologists in Hubli as part of its expert team. These experts specialise in providing holistic care for various neurological conditions through personalised and patient-focussed approaches.
Medical Management
In medical practice, the Alzheimer's treatment process entails symptom control aimed at slowing down the disease progression. Various drugs and non-pharmacological therapies are used by our neurologists at HCG Suchirayu:
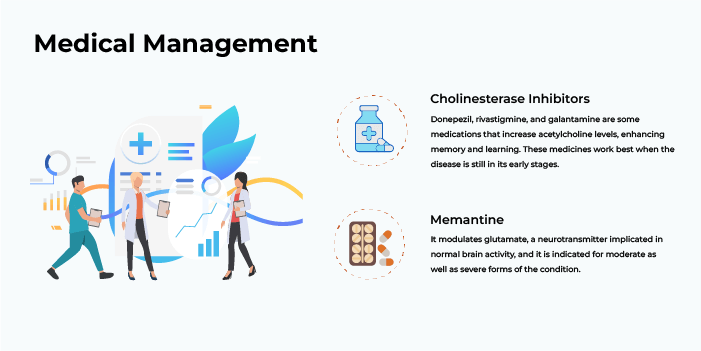
Cholinesterase Inhibitors: Donepezil, rivastigmine, and galantamine are some medications that increase acetylcholine levels, enhancing memory and learning. These medicines work best when the disease is still in its early stages.
Memantine: It modulates glutamate, a neurotransmitter implicated in normal brain activity, and it is indicated for moderate as well as severe forms of the condition.
Benefits: They enhance memory, attentiveness, and decision-making.
Side Effects: Occasionally, patients may feel nausea, vomiting, or dizziness after taking these medications.
Emerging Treatments:
Anti-Amyloid Drugs: Research is underway to produce drugs targeting amyloid plaques, which are typical signs seen in Alzheimer’s patients. A few experimental therapies are aimed at decreasing or preventing such deposits in the brain.
Non-Pharmacological Interventions: Psychotherapies, social involvements, and lifestyle changes are gaining more importance as part of the Alzheimer's treatment process. There have been promising findings from certain techniques like brain-training exercises as well as art therapy.
Managing Symptoms and Improving Quality of Life
Symptom Management:
Strategies for Managing Behavioral and Psychological Changes: To manage restlessness and memory loss, one can apply techniques such as structured routines, calming environments, and behaviour modifications.
Techniques for Improving Daily Living Activities: There are occupational therapies as well as memory aids that could help one carry out their normal duties effectively.
Enhancing Quality of Life:
Role of Caregivers and Family: Teaching caregivers how to deal with changing moods and problems with communication and promoting independence can make a big difference in the care given.
Coordination with Health Care Professionals: Seeing neurologists, psychologists, and occupational therapists regularly ensures that all aspects of care are covered.
Support Services in Hubli
Local Support Services: In Hubli, there are various support groups and facilities for families who have patients with Alzheimer’s disease, such as respite care and counselling.
Finding a Neurological Specialist: When looking for a specialist, consider someone who has experience with dementia care and can access up-to-date treatments and technology. HCG Hospitals is Hubli's super speciality hospital known for its neurological expertise.
Accessing Neuro Care in Hubli
HCG Neuro Care: HCG Suchirayu Hospital, which is sometimes referred to as HCG Hospital, is equipped with modern facilities to diagnose, treat, and manage different types of neurological conditions with an individualised and patient-centric approach, where both the clinical outcome and the overall well-being of the patient are equally prioritised.
HCG Suchirayu Hospital is known for its multidisciplinary care approach, wherein experts from multiple disciplines study each case diligently before recommending a comprehensive treatment plan, which is devised based on individual patient needs.
How to Schedule an Appointment: Patients can book appointments easily through the hospital website (www.hcghospitals.in) or call on the hospital’s centralised call centre number, +91 74064 99999. Patients and their caregivers can consult the specialist of their choice on the date and time that is convenient for them.
Conclusion
To sum up, early recognition, efficient medication, and all-rounded attention are important in dealing with Alzheimer’s disease. These are available through the neurological department of HCG Suchirayu Hospital in Hubli, where the expert team perfectly blends modern treatment approaches with compassionate care. Through this, they make work for the betterment of Alzheimer's effects, managing Alzheimer's symptoms, dealing with behavioural change, and providing continuous patient and caregiver support.
 Cardiothoracic and Vascular Surgery
Cardiothoracic and Vascular Surgery Clinical Immunologist
Clinical Immunologist Clinical Nutrition
Clinical Nutrition Dermatology Department
Dermatology Department Emergency Medicine
Emergency Medicine Endocrinology
Endocrinology