Home / Blog / Types of Angina: Stable, Unstable, and Variant Angina Explained
Table of Contents
Angina is chest pain or discomfort that happens when the heart muscle doesn’t get enough blood. It’s a common symptom of heart disease. It is important to understand that there are different types of angina, each with distinct causes, symptoms, and management strategies.
In this blog post, you will find information on three main types of angina pectoris: stable angina, unstable angina, and variant angina (Prinzmetal’s angina). By understanding these variations, you can take the necessary steps for effective management and treatment.
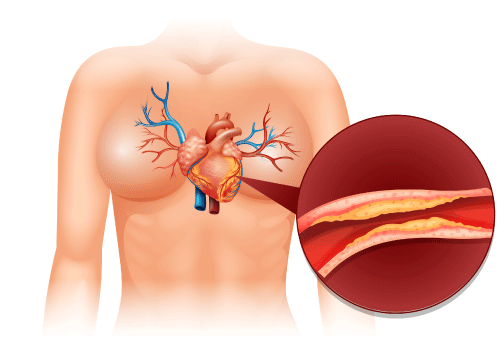
Angina is chest pain or discomfort caused by decreased blood flow to the heart muscle, usually due to blockage or narrowing of the coronary arteries. It often manifests as heaviness, tightness, or pressure across the chest that may radiate into the arms, neck, jaw, or back. There are three main kinds of angina:
These variations differ in their triggers, symptoms, and severity.
Definition: Stable angina is the most common form of angina. It happens when the heart’s oxygen demand increases during physical activity, emotional stress, or after heavy meals, but narrowed arteries can’t supply enough blood.
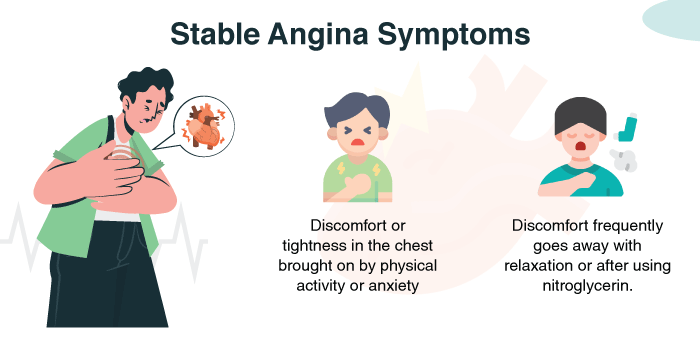
Stable angina can usually be managed with the right treatment and lifestyle changes.
Title tag: Unstable Angina
Alt tag: Unstable Angina
Definition: Unstable angina is a more severe and less predictable type of angina. It can happen unexpectedly, sometimes while you’re at rest, and might last longer than stable angina. Unstable angina is considered a medical emergency.
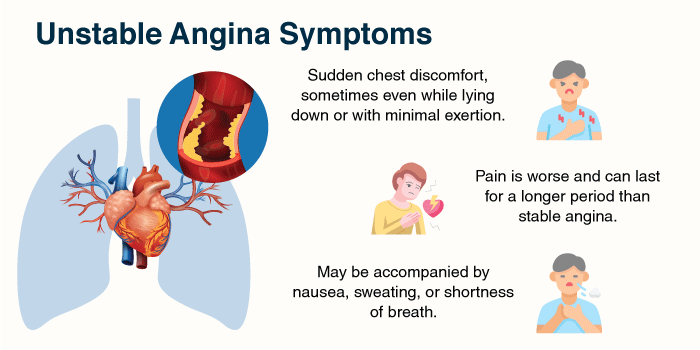
Unstable angina considerably raises the chance of a heart attack and requires quick diagnosis and treatment.
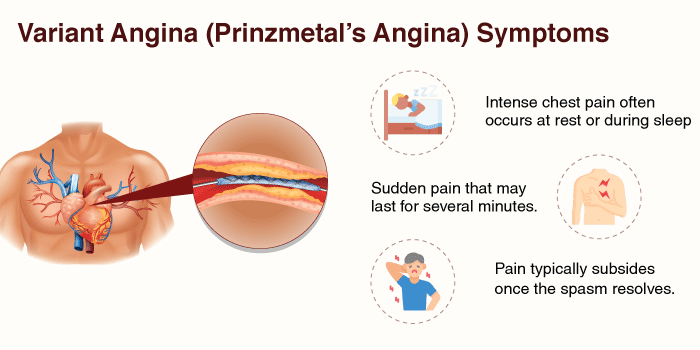
Definition: Variant angina, which is also called Prinzmetal’s angina, is an unusual type of angina pectoris. It occurs when spasms in the coronary arteries temporarily limit blood flow to the heart muscle.
When treated correctly, variant angina can be managed effectively; moreover, the risk of heart attacks is lower than with other forms of angina.
The following are the different management strategies available for angina pain:
Angina pectoris is a severe condition resulting from decreased cardiac blood flow and has three main types: stable angina, unstable angina, and variant angina. It is crucial to recognise the causes and symptoms of these so that they can be managed effectively. If you experience chest pain or suspect you may have angina, talk to the cardiac experts at HCG hospitals. We are one of the best multispeciality hospitals in India, with locations in Ahmedabad, Bhavnagar, Hubli, and Rajkot. Visit our cardiology speciality page to learn more about our comprehensive heart care services: HCG Hospitals: Best Heart Hospital in India.