
Home / Blog / Top Conditions Treated by Hepatologists and Gastroenterologists
Table of Contents
The liver, the second-largest organ in your body, performs around 500 functions, and so liver health is equivalent to your life quality.
A good digestive system ensures you get optimum energy and nutrients from what you eat and drink. If your digestive health is threatened, your overall health is in danger.
Hepatology is a branch of medicine dedicated to the diagnosis, treatment, and management of diseases that affect the liver, gallbladder, bile ducts, and pancreas.
Hepatitis, ALD, NAFLD, cirrhosis, and liver cancer are typical hepatology diseases managed by a hepatologist.
Gastroenterology is a branch of medicine dedicated to the diagnosis, treatment, and management of diseases that affect the gastrointestinal tract and related organs.
IBS, GERD, peptic ulcer, pancreatitis, and coeliac disease are digestive disorders typically managed by gastroenterologists.
The inflammation of the liver is called hepatitis. It can be caused by viruses, chemicals, drugs, alcohol, genetic disorders, or even a hyperactive immune system.
There are five strains of the hepatitis virus: A, B, C, D, and E.
Based on the severity of the disease, different treatment options are recommended for hepatitis.
People recover from acute hepatitis A and B and acute hepatitis E with rest and a nutritious diet. Chronic hepatitis B is treated with antiviral drugs. In severe cases, a liver transplant may be necessary.
Direct-acting anti-virals DAAs are given to resolve acute and chronic hepatitis C.
Both acute and chronic hepatitis D are usually treated with PEG-IFNα, a form of interferon.
Antiviral drugs are the first line of treatment for chronic hepatitis E.
Cirrhosis is a progressive liver condition in which healthy liver cells are gradually replaced by scar tissue due to chronic hepatitis.
In the initial stage, a severely scarred liver is still able to function. It is called compensated cirrhosis.
In the advanced stage, liver function declines further and is known as decompensated cirrhosis.
Depending on the extent of the disease, different treatment approaches are recommended to treat liver cirrhosis. Lifestyle modifications, medications, and liver transplantation are commonly recommended treatment options for this condition.
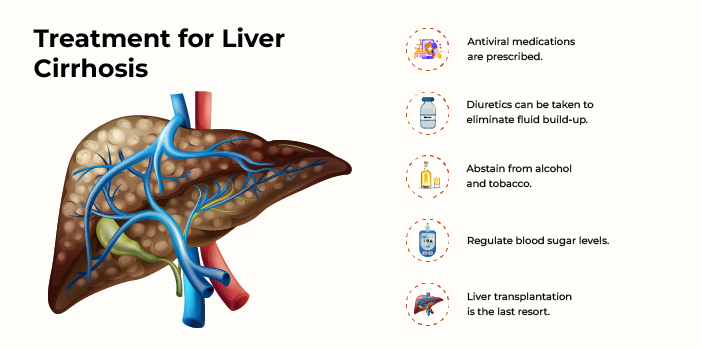
If you are looking for the best doctor for cirrhosis with great expertise and good patient outcomes, you may reach out to HCG Hospitals, a leading multispeciality hospital in India.
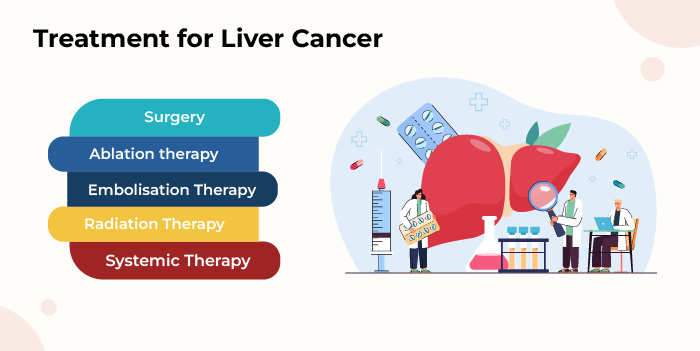
Liver cancer refers to the condition where the liver cells undergo mutations and start dividing uncontrollably to form a mass or tumour.
Liver cancer is best managed when it is detected and treated in the early stages.
Liver cancer is treated with a personalised treatment approach, wherein oncologists will create a treatment plan upon considering various factors like the type of liver cancer, its stage and grade, the exact location, the shape of the tumour, the patient’s age, the overall health, and lastly, their preferences.
Fatty liver disease refers to the condition where there is abnormal fat accumulation in the liver due to the organ’s inability to process fats adequately. There are two types of fatty liver disease: non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD).
NAFLD may start as a simple fatty liver (steatosis) and can advance to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). NASH can lead to liver cirrhosis and even liver cancer. NAFLD is caused by fat accumulation in the liver. It is often seen in people who are obese or overweight.
AFLD occurs when excessive alcohol consumption leads to fat buildup in the liver. Fatigue, vomiting, itchy skin, swollen stomach, and legs are common symptoms of liver disease.
Consult the best liver specialists at HCG Hospitals for more information on maintaining good liver health.
A liver transplant is a major surgery done to substitute a damaged liver with a healthy one obtained from a donor.
It is recommended to manage cirrhosis-related conditions, such as ascites, variceal bleeding, and hepatic encephalopathy. It may also be recommended for patients with liver cancer.
Before the liver transplantation, the donor and receiver will undergo a series of tests in order to increase the chances of a successful liver transplant, and some of them include:
After the liver transplant, patients should pay extra attention to their health and follow their doctor’s recommendations in order to reduce the risk of organ rejection.
Consuming a balanced diet, adhering to follow-up appointments, looking out for signs of organ rejection and infection, and reducing infection risk are a few measures one must take during the initial few months after the transplant.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome, or IBS, is a chronic and relapsing condition that is associated with the digestive tract. IBS is triggered by an imbalance in gut bacteria, inflammation, stress, and certain foods.
Stomach pain, diarrhoea, constipation, and bloating are some of the IBS symptoms.
Make a list of foods and drinks that trigger IBS episodes and avoid them for the sake of your gut health.
Find activities to manage stress levels. Consult your doctor if you suspect any of your medications are triggering your IBS.
If you are looking for the best gastroenterologist in India, you may reach out to HCG Hospitals.
Gastroesophageal reflux is a digestive health condition that occurs when stomach acid frequently moves back into the oesophagus (the tube that links the mouth to the stomach).
Heartburn, sour taste in the mouth, and difficulty swallowing are some of the common symptoms of GERD.
Eat whole grains, lean meats, non-citrus fruits and vegetables. Avoid fast, spicy, and fried food.
Doctors usually prescribe drugs that reduce the production of stomach acid.
A minimally invasive surgery to implant a LINX device that blocks the refluxing acid is recommended in some cases.
A peptic ulcer is a lesion on the inner lining of the upper digestive system.
Peptic ulcers are caused by a bacterium (Helicobacter pylori) and long-term use of certain anti-inflammatory medicines like aspirin and ibuprofen.
Stomach pain, belching, bloating, and bloody stools are the symptoms of peptic ulcer.
Doctors prescribe antibiotics to treat H.pylori. Stomach-acid-reducing medicines are also given to the patients.
Go for a fibre-rich diet with non-acidic fruits and vegetables to manage your digestive health condition.
Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas.
Acute pancreatitis is a sudden inflammation of the pancreas. It is usually caused by gallstones and alcohol consumption.
Chronic pancreatitis is the progressive inflammation of the pancreas. Repeated episodes of acute pancreatitis lead to chronic pancreatitis.
Intense stomach ache, vomiting, increased heart rate, and low BP are a few symptoms of the condition.
Pain-blocking medications are given to people with chronic pancreatitis. Sometimes, damaged parts of the pancreas are removed via surgery.
Avoid alcohol, smoking, and processed food.
Coeliac disease is a chronic and genetic autoimmune disorder that mainly impacts the small intestine. It is triggered by gluten, a protein found in wheat, rye, and barley.
Chronic diarrhoea or constipation, abdominal gas, weight loss, anaemia, and tingling in the legs are some of the symptoms of coeliac disease.
Read the labels of packaged foods and avoid gluten-containing food items. Eat only gluten-free grains like rice, ragi, and quinoa. Check with your healthcare provider if there is a need for additional supplements.
If you start experiencing any gastrointestinal symptoms persistently, you should see a doctor for a prompt evaluation, where a gastroenterologist or liver specialist will carefully examine you to determine the underlying cause and recommend appropriate treatment.
Being the top gastroenterology hospital in India, HCG treats thousands of people suffering from digestive disorders every year and positively contributes to their overall well-being.
Drop in a message for an appointment on the chatbot on the HCG Hospitals website. We will contact you immediately.
A gastroenterologist focusses on diagnosing and treating digestive disorders. A hepatologist is a gastroenterologist with advanced training and specialisation in liver diseases.
You should see a hepatologist if you are suffering from illness of the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, and bile ducts. If you notice symptoms of viral hepatitis, ALD, NAFLD, cirrhosis, liver cancer, etc., please see a hepatologist.
Blood tests, imaging tests, biopsies, endoscopies, and colonoscopies are some of the tests used by hepatologists and gastroenterologists.
Gastro-oesophageal reflux is a digestive health condition that occurs when stomach acid frequently moves back into the oesophagus (the tube that links the mouth to the stomach). Doctors usually prescribe drugs that reduce the production of stomach acid.
Typically, you can visit your specialist doctor for a follow-up appointment every three to six months. During a flare-up, more frequent appointments might be necessary to adjust medications and address symptoms effectively.
Consult a gastroenterologist for treatment of digestive disorders like acid reflux, ulcers, IBS, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and colorectal cancer.
Eat leafy greens to optimise the liver’s role of detoxifying your body. Stay hydrated so that the liver can easily flush out toxins. A high-fibre diet is a natural treatment for digestive disorders. Have a diverse range of food for a variety of nutrients.
New medications have been developed to treat certain liver conditions and GI conditions. More advanced treatment approaches, such as minimally invasive surgery, organ preservation surgery, etc., are available today to manage a broad range of GI conditions effectively.
Abstinence is one of the crucial lifestyle changes recommended to manage liver disease. Eat a nutritious diet that works well for your immunity. Exercise regularly and maintain a healthy weight. Avoid smoking and all tobacco products.
Chronic hepatitis B is treated with antiviral drugs. In severe cases, a liver transplant may be necessary. Direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) are given to resolve acute and chronic hepatitis C. Acute and chronic hepatitis D are usually treated with PEG-IFNα (a chemically modified form of a natural protein that strengthens the immune system). Antiviral drugs are the first line of treatment for chronic hepatitis E.