
Home / Blog / Pyrexia (Fever): Causes, Symptoms, Treatment & When to See a Doctor
Table of Contents
Pyrexia, commonly known as fever, is characterised by the body’s innate response to infections or illnesses and is characterised by rises in temperature above the normal level of 98.6°F (37°C) in the body. While fever in itself is not an illness, it is known to stem from a variety of underlying health conditions.
The objective of this blog is to give a general idea about all causes, fever symptoms, treatments, and options for seeking a health professional’s advice in case of pyrexia.
Medically, pyrexia refers to an elevated body temperature, as elevated as above the normal threshold of 98.6 degrees F (37°C). It is often triggered by infections or other health conditions and serves as a physiological response to combat harmful agents. Unlike hyperthermia, pyrexia is controlled by the body and not by any external factors like exposure to hot temperatures.
Fever is not a disease but a symptom, highlighting the body’s defence mechanism against infections.
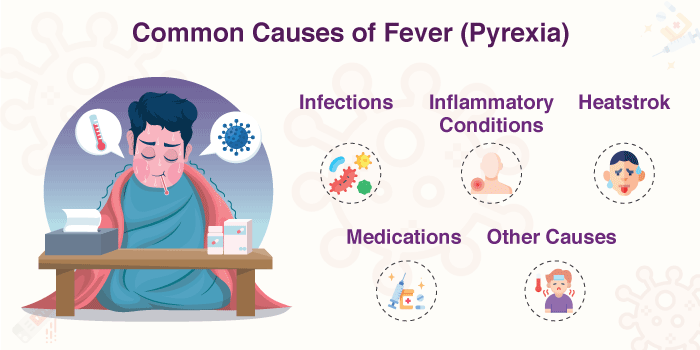
Most of the time, fever develops because an inflammatory condition such as rheumatoid arthritis or inflammatory bowel disease can reach chronicity in the human body.
In some cases, a heatstroke can cause fever. Avoiding extremely high temperatures and staying well hydrated can help prevent heatstroke.
Certain drugs, including antibiotics and vaccines, can induce temporary fever as a side effect.
Fever can also result from cancer, severe dehydration, or tissue damage from injuries.
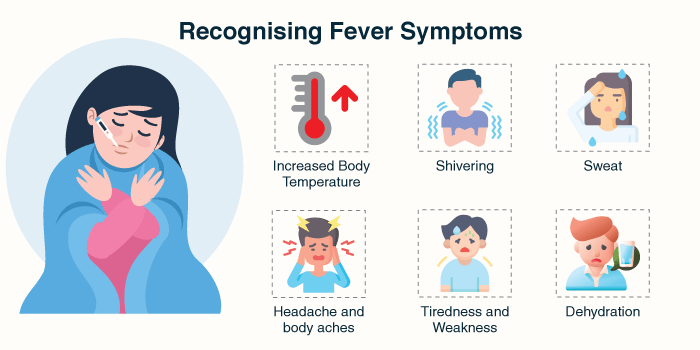
Detecting fever in children can be difficult, but it’s important to monitor their behaviour and fever temperature closely. Children less than three months with fever are to be consulted with a paediatrician in any doubt.
Medications should be used for comfort or if the fever exceeds 103°F (39.4°C). Always follow medical advice for persistent or high-grade fever.
Warning Signs: Always consult your doctor if the fever exceeds 104°F (40°C) and lasts for more than three days, and also when accompanied by severe fever symptoms, such as difficulty breathing, a rash, or persistent vomiting.
Infants and Young Children: Fever in infants younger than three months is considered an emergency. For older children, consult a doctor if fever persists or is accompanied by lethargy or irritability.
Underlying Health Conditions: Individuals with chronic conditions or weakened immune systems should seek prompt medical care.
Consulting a doctor: Visit HCG Hospitals for expert care and thorough evaluation to determine the underlying cause of pyrexia.
Understanding pyrexia is essential for recognising potential health issues. Fevers usually will simmer down when proper care is taken, but if persistently or severely felt, symptomatic measures should warrant medical intervention. Educating oneself about the fever symptoms and monitoring them promptly is another way of preventing several problems. If the fever persists or worsens, make an appointment at the HCG Hospitals for professional diagnosis and fever treatment.