Home / Blog / Lymphocytosis (High Lymphocyte Count): Causes, Symptoms, and When to Worry
Table of Contents
Lymphocytosis is an increased number of lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell, in the blood. Lymphocytes are essential for the immune system, enabling the body to fight off infections and other threats. While lymphocytosis does not always indicate a problem, it can sometimes indicate underlying health issues such as infection, autoimmune diseases, or leukaemia.
This blog explores the cause, lymphocytosis symptoms, and lymphocytosis treatment options and guides when to seek treatment.
Lymphocytes are an important immune system component, protecting against infectious agents such as viruses and bacteria. Lymphocytosis refers to a higher-than-normal number of lymphocytes in the blood, usually detected during routine blood tests.
There are two types of lymphocytosis:
Recognising these differences is important to understanding the significance of the situation.
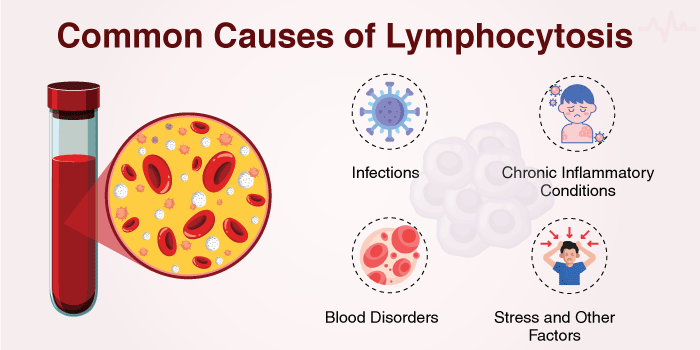
Autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus cause lymphocytosis because the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue, causing inflammation.
Certain types of leukaemia, including chronic leukaemia and lymphoma, result in uncontrolled lymphocyte production, leading to increased rates of lymphocytosis.
Physical or emotional stress, certain medications, and smoking can slightly increase lymphocytosis levels.
Many individuals with lymphocytosis have no obvious symptoms. It is usually diagnosed during routine blood tests for other reasons.
Symptoms associated with causes
In cases of blood cancers, lymphocytosis symptoms may include night sweats, unexplained anaemia, or extreme fatigue. These cases prompt immediate medical attention.
A complete blood count (CBC) is the primary diagnostic tool for lymphocytosis, measuring the number and quality of white blood cells.
If lymphocytosis is diagnosed, additional tests such as a viral panel, lymphocyte count, and bone marrow biopsy may be needed to establish the root cause.
Additional tests help distinguish between mild infections and severe conditions, such as leukaemia, and more accurately lymphocytosis diagnosis.

For mild cases or situations where the cause is not serious, routine and follow-up blood tests may suffice as an effective lymphocytosis treatment strategy.
Although lymphocytosis is not always dangerous, symptoms such as unexplained weight loss, persistent fever, night sweats, cough, or varicose veins warrant further investigation.
If you have severe symptoms such as abnormal bleeding and prolonged fatigue, seek medical advice.
For individuals with the diagnostic conditions of lymphocytosis, regular monitoring of the condition and adherence to treatment regimens are necessary to effectively manage the condition.
Lymphocytosis can be caused by a variety of factors, including infection, autoimmune diseases, and leukaemia. While it can usually be asymptomatic, it can also indicate serious health issues. Understanding the lymphocytosis symptoms and seeking medical advice on time is essential for proper lymphocytosis diagnosis and treatment. If you have concerns about your lymphocyte count or related symptoms, consult a specialist at HCG hospitals for proper care.