Shortness of breath, medically defined as dyspnoea, is a sensation of difficulty breathing or the inability to get enough air. It is a common symptom that can range from mild to severe and can be caused by various underlying health conditions. The experience of dyspnoea can be alarming, and understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments is important for effective management. This blog examines the most common causes of shortness of breath, highlights symptoms, and discusses treatments to alleviate this condition.
What is Shortness of Breath (Dyspnoea)?

Definition of Dyspnoea
Dyspnoea is a medical term for shortness of breath. It is often described as trouble breathing, feeling like one cannot get a full breath, and/or laboured breathing.
Types of Dyspnoea
- Acute dyspnoea: An abrupt and intense problem with inhaling and exhaling that could be a sign of a serious health condition.
- Chronic dyspnoea: Long-lasting or recurring breathing problems for weeks or months are usually associated with other illnesses.
When Should You Worry?
Immediate medical attention is necessary if a person suddenly experiences shortness of breath or has other signs like:
- Chest pain or pressure
- Fainting or dizziness
- Bluish lips or fingertips
- Severe difficulty breathing, even at rest
Also Read: How to Prevent Heart Disease: Tips for a Stronger, Healthier Heart
Common Causes of Shortness of Breath (Dyspnoea)
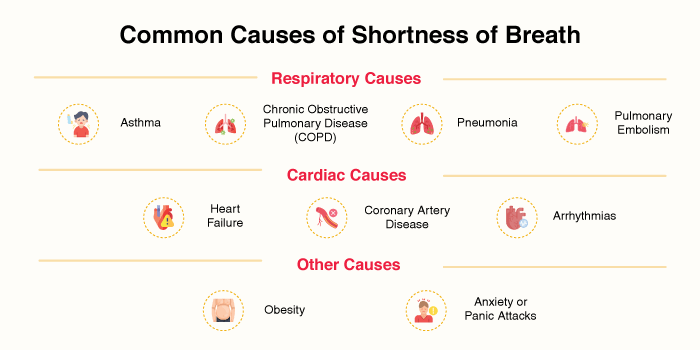
Respiratory Causes
- Asthma: Airway inflammation and constriction occur, causing shortness of breath. Wheezing and a tight chest.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): People with emphysema and chronic bronchitis have persistent dyspnoea because their lungs cannot take in enough air due to low lung capacity and poor airflow.
- Pneumonia: Infections cause swelling of lung tissue and hinder oxygen exchange, leading to breathlessness.
- Pulmonary Embolism: A blood clot in the lungs can stop blood from flowing, causing sudden and severe shortness of breath.
Cardiac Causes
- Heart Failure: Fluid buildup in the lungs due to heart failure can cause dyspnoea, especially when lying down.
- Coronary Artery Disease: When the arteries become smaller, blood flow to the heart and lungs is reduced, causing problems in breathing.
- Arrhythmias: Irregular heartbeats limit oxygenated blood flow, triggering dyspnoea.
Other Causes
- Obesity: Excess weight strains the heart and lungs, making breathing more laborious.
- Anxiety or Panic Attacks: Feeling stressed or anxious may cause hyperventilation and a sensation of shortness of breath.
Symptoms of Shortness of Breath (Dyspnoea)
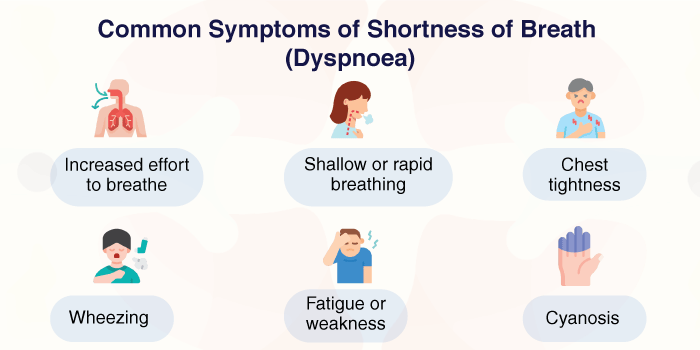
Common Symptoms
- Increased effort to breathe: A feeling of working harder to inhale or exhale.
- Shallow or rapid breathing: Breathing quickly without full breaths.
- Chest tightness: A common symptom in asthma- or anxiety-induced dyspnoea.
- Wheezing: A whistling sound when exhaling, often seen in asthma or COPD.
- Fatigue or weakness: Insufficient oxygen can make you feel lightheaded or tired.
- Cyanosis: A bluish tinge to the lips or fingertips due to reduced oxygen levels.
Differentiating Symptoms
- Heart-related dyspnoea: This is most of the time seen with oedema in the lower limbs, angina, or syncope.
- Lung-related dyspnoea: It generally involves difficulty breathing with phlegm, coughs, or wheezes.
Symptoms Based on Severity
- Mild dyspnoea: Breathlessness that goes away after taking a break experienced only during strenuous exercise.
- Severe dyspnoea: It is hard to breathe while resting or during minimal exertion, and one must seek medical attention as soon as possible.
Also Read: How Coronary Artery Disease Affects Your Heart: A Doctor’s Guide
When to Seek Medical Help for Shortness of Breath
Immediate Warning Signs
Seek urgent medical care if you experience:
- Breathlessness is very serious and comes with pain or tightness across the chest.
- Unexpected dyspnoea that occurs suddenly for no known reason.
- Signs of a heart attack, e.g., discomfort spreading towards the mandible, upper limb, or dorsal side.
- Increased dyspnoea on exertion, syncopal episode, or oedema that progresses with time.
Importance of Early Intervention
Getting medical help quickly can assist in identifying the reasons for shortness of breath and avoiding problems.
Diagnosis of Shortness of Breath (Dyspnoea)
Physical Examination
Doctors evaluate breathing patterns, listen to the lungs and heart sounds, and measure oxygen levels to determine if there is a need for shortness of breath treatment.
Diagnostic Tests
- Chest X-ray: It can show if there are any problems with the lungs, such as infections, fluids, or structure.
- Pulmonary function tests: Identify conditions like asthma or COPD.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): It helps to know that it is not due to heart disease.
- Blood Tests: They are done to check if there is a low level of blood in the body system, the presence of infections, or any other abnormality.
- CT Scan: It gives clear pictures that can be used to identify and diagnose problems such as pulmonary embolism or severe lung disease.
Also Read: Understanding Cholesterol and Its Role in Coronary Artery Disease
Treatment for Shortness of Breath (Dyspnoea)
Treatment Based on the Cause
- Respiratory Treatments:
- Inhalers for asthma or COPD to open airways.
- Oxygen therapy for chronic lung conditions.
- Antibiotics or antivirals for pneumonia.
- Cardiac Treatments:
- Heart medications such as diuretics, beta-blockers, or ACE inhibitors.
- Surgery like angioplasty is done for coronary artery blockages.
- Other Treatments:
- Losing weight to ease difficulty in breathing caused by being overweight.
- Breathing exercises, like pursed-lip breathing, can help anxiety-induced shortness of breath.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Diet and Exercise: Improve overall lung and heart health.
- Stress Management: Practices such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing can help in lessening the signs of anxiety.
- Medications for Anxiety: People who are always anxious may need to take anti-anxiety medications or go for counselling.
Preventing Shortness of Breath (Dyspnoea)
Managing Risk Factors
- Avoid smoking and maintain a healthy weight.
- Control high blood pressure and cholesterol.
- Stay active by exercising often to make your heart and lungs stronger.
- Take flu and pneumonia vaccinations to lower the chances of respiratory infections.
Breathing and Stress Management
- Do breathing exercises often to improve lung capacity.
- Control anxiety attacks by using relaxation methods.
Conclusion
The causes of shortness of breath can vary, such as diseases of the respiratory system or heart, anxiety, and lifestyle. Recognising shortness of breath symptoms and promptly going for medical check-ups and medication can greatly improve quality of life. If you or someone you know cannot breathe well for long without any reason, call a doctor immediately. Taking proactive steps to address risk factors and seeking appropriate treatment can significantly improve quality of life and overall health. Visit the Best Pulmonology and Heart Hospitals in India, located in Hubli, Bhavnagar, Rajkot, and Ahmedabad, for expert care and treatment.




