Home / Blog / Understanding Cholesterol and Its Role in Coronary Artery Disease
Cholesterol plays a vital role in the functioning of the human body. Yet, its imbalance is a leading factor in coronary artery disease (CAD), a major cause of heart attacks and strokes worldwide. Many people do not know that cholesterol affects the health of the heart.
For an in-depth understanding of CAD, its causes, and its symptoms, click on the link here to our educational blog on “What is Coronary Artery Disease? Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment”
In this article, we will discuss cholesterol and heart disease, cholesterol and heart disease correlation, and practical ways to maintain a healthy balance.
Every cell in the body contains a fat substance known as cholesterol. The body needs it to make hormones, vitamin D, and other components necessary for digestion. Nevertheless, cholesterol is of two primary kinds:
It is important to balance these types because an excess of LDL or a deficiency of HDL may affect heart health.
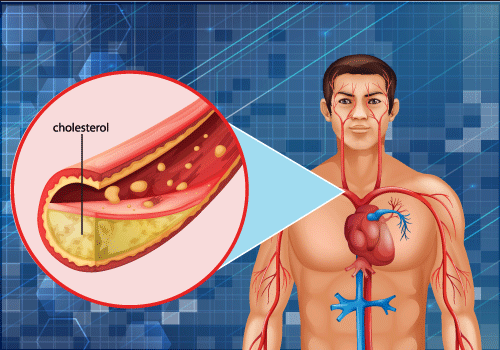
If the level of LDL cholesterol in the bloodstream is too high, it can deposit along the walls of the coronary arteries, forming a sticky substance called plaque. The plaque becomes hard with time, and this leads to the narrowing of the arteries, hence reducing the blood supply to the heart.
Atherosclerosis is the first stage of coronary artery disease. When plaque breaks, it may form a clot; it can cause a blood clot, potentially leading to a heart attack or stroke.
Cholesterol and heart disease correlation is well documented. Elevated LDL cholesterol levels significantly increase the risk of coronary artery disease, while adequate HDL levels can lower it. Here’s how:
This complex correlation between cholesterol and heart disease shows how vital it is to control cholesterol levels properly.
There are many things that affect the amount of cholesterol in your blood. Some of these factors are controllable while others are not.
1. Genetics: Your family history plays a significant role in determining cholesterol levels. If your family has a history of high cholesterol, then you are at a greater risk of hypercholesterolemia and CAD.
2. Age: As people grow older, they need to check their cholesterol levels more often because they are likely to increase.
1. Diet: Eating excess saturated fats and trans fats is bad because it raises LDL. Replacing these with healthier fats and fibre-rich foods can help.
2. Physical Activity: Regular physical activity can reduce LDL and increase HDL levels, promoting cardiovascular fitness.
3. Lifestyle Choices: Smoking, too much drinking, and being stressed lead to high levels of bad fat in the blood. Stopping smoking and controlling stress may have a big impact.

Routine cholesterol checks are crucial for preventing coronary artery disease. Here’s why:
Doctors usually advise a lipid profile test, which measures total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, and triglycerides.
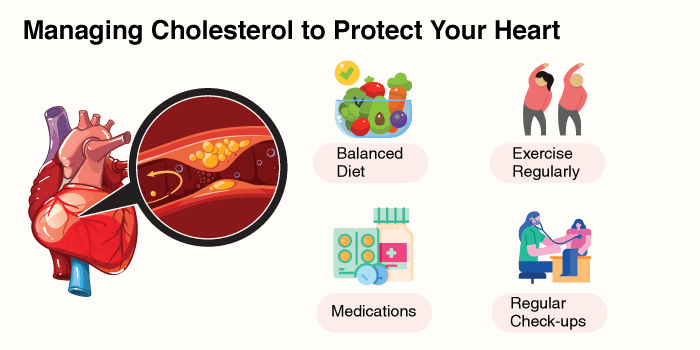
To reduce the impact of cholesterol on heart health, consider these practical steps:
Collaborate with your doctor to keep track of your cholesterol levels and make necessary lifestyle changes.
Cholesterol is necessary for various bodily functions; it can become dangerous if present in excess quantities. The way it is linked to coronary heart disease shows why it is crucial to have good levels of cholesterol to avoid heart diseases as well as lower chances of getting heart attacks and strokes.
To take charge of your cardiac health, begin with checking cholesterol levels regularly, adopting a lifestyle that promotes good health, and seeking medical advice when necessary.
For more insights on coronary artery disease and heart health, explore our related articles:
Take charge of your heart health today!