Home / Blog / Critical Signs of Dengue Fever: What You Need to Know to Act Fast
Table of Contents
In the last few decades, there has been a steep rise in the incidence of dengue worldwide, with cases reported to WHO increasing from 505,430 cases in 2000 to 5.2 million in 2019.
Since early 2023, ongoing transmission with an unexpected increase in cases of dengue has pushed the number to the highest peak ever of over 6.5 million cases, with more than 7300 deaths attributed to the disease.
In the last two decades in India, the number of cases increased 11-fold, and repeated outbreaks occurred.
Patients with mild dengue fever experience a high fever, a severe headache, and joint and muscle pain. If left untreated, mild dengue fever might progress to dengue haemorrhagic fever and dengue shock syndrome.

Mild dengue fever symptoms include high fever, nausea and vomiting, severe headache, fatigue, pain behind the eyes, joint and muscle pain, fatigue, skin rash, and mild bleeding.
Some of the vital signs that require immediate medical attention are:
Dengue fever causes severe abdominal pain, and the possible reasons for this may include plasma leakage, involvement of the liver, gastrointestinal bleeding, and pancreatitis.
Severe dengue fever causes persistent vomiting, which may lead to dehydration and electrolyte imbalance.
Dengue fever causes bleeding gums and nosebleeds, especially in advanced cases. They may be caused by a low platelet count, coagulation disorders, or vascular damage.
Dengue fever causes vomiting blood (hematemesis) or passing black stools (melena), which are associated with significant internal bleeding. It typically occurs in the more severe forms of dengue, i.e., dengue haemorrhagic fever and dengue shock syndrome.
Most patients with dengue fever exhibit a characteristic feature of lethargy or a lack of energy, which may sometimes be identified in both mild and severe forms. Sometimes, it affects their quality of life and indicates the disease’s progression.
Dengue fever causes difficulty breathing. It may be due to plasma leakage, fluid overload, organ failure, bleeding, high fever, and dehydration.
Cold or clammy skin is a concerning symptom of dengue, which usually includes severe diseases like Dengue Shock Syndrome. This usually results from poor blood circulation and shock and requires immediate medical attention.
Early action in patients with dengue is essential to prevent complications. Some of the potential complications of severe dengue are:
Patients can experience significant internal bleeding, including gastrointestinal bleeding, bleeding gums, nosebleeds, and bleeding into the skin. Severe bleeding can lead to hypovolemic shock and death if not promptly treated.
If not managed promptly with intravenous fluids and supportive care, shock can lead to multi-organ failure and death.
Patients with severe dengue may experience failure of various organs, such as the liver and kidney. The patients may also have cardiovascular collapse, respiratory failure, and acute respiratory distress syndrome.
Dengue may also cause neurological complications in patients with severe dengue. These include seizures, encephalitis, and coma.
Excessive fluid loss and intravenous fluid administration can lead to low sodium levels, causing confusion, seizures, and neurological impairment. Severe dehydration and shock can lead to metabolic acidosis, where the blood becomes too acidic, affecting organ function.
Patients are at risk of secondary bacterial infections because of compromised immune systems. Secondary infections may lead to sepsis, which is a life-threatening condition that may cause systemic inflammation and organ dysfunction.
Early diagnosis and timely treatment are crucial for effective dengue management. Early diagnosis helps prevent the disease from progressing to advanced stages when treatment becomes challenging.
Early diagnosis of dengue fever is essential for managing and avoiding severe complications.
Early diagnosis supports effective dengue fever treatment and close monitoring to prevent it from developing into a severe disease with possible complications.
Early diagnosis enables watching for warning signs of dengue: intense abdominal pain, persistent vomiting, bleeding, and breathlessness.
Fluid balance management in dengue is important to prevent Dengue Shock Syndrome. Early dengue fever treatment ensures effective fluid management, maintaining proper hydration, and preventing severe dehydration and shock.
Early diagnosis is also essential for the management of platelet level and coagulation problems, another important aspect of reducing the risks of severe bleeding complications related to dengue haemorrhagic fever.
Early dengue fever treatment makes the disease milder in its course, thus reducing mortality and severe complications and promoting a faster recovery.
In addition, it may reduce the length of hospitalisation and speed up recovery. Timely treatment is also crucial to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
Early diagnosis enables individualised support with appropriate fluid therapy, better pain management, and monitoring for the emergence of complications. This would greatly improve recovery rates and reduce the risk of bad outcomes.
If the patients experience severe dengue symptoms, they should immediately consult with healthcare providers to prevent life-threatening symptoms, including organ failure.
Patients may reach out to specialists at HCG for immediate medical attention.
As a leading multispeciality hospital in Ahmedabad, HCG Hospitals has advanced facilities for prompt diagnosis and care for patients with dengue-associated serious complications. HCG hospitals offer the services of general physicians and infection specialists.
To easily find and consult a dengue specialist near you, you may Google “dengue doctor near me” or “dengue specialist near me” and contact them for immediate assistance.
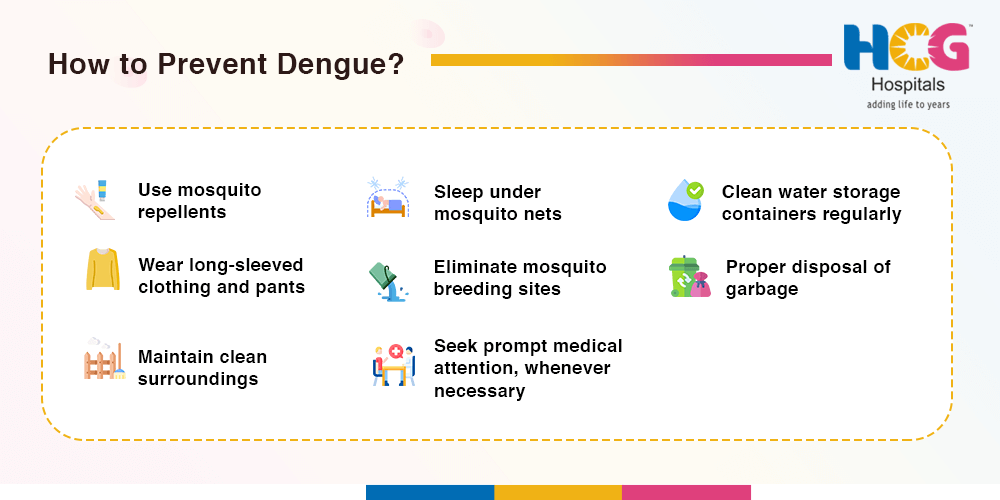
Dengue mosquitoes are active during the day. It is important to reduce the risk of contracting dengue by following protective measures against mosquito bites.
Some of these protective measures include using window screens, covering most of the body parts through clothes, using mosquito repellent creams, vaporizers, and coils, and using mosquito nets during sleep.
Another measure to prevent dengue is to stop mosquito breeding. It may be done through environmental modification and management to avoid creating a favourable environment for mosquitoes to lay eggs.
To avoid mosquito breeding, one should consider emptying, cleaning, or covering the water storage containers frequently, properly disposing of the solid wastes, removing the water-holding areas, and using appropriate insecticides in the containers storing water.
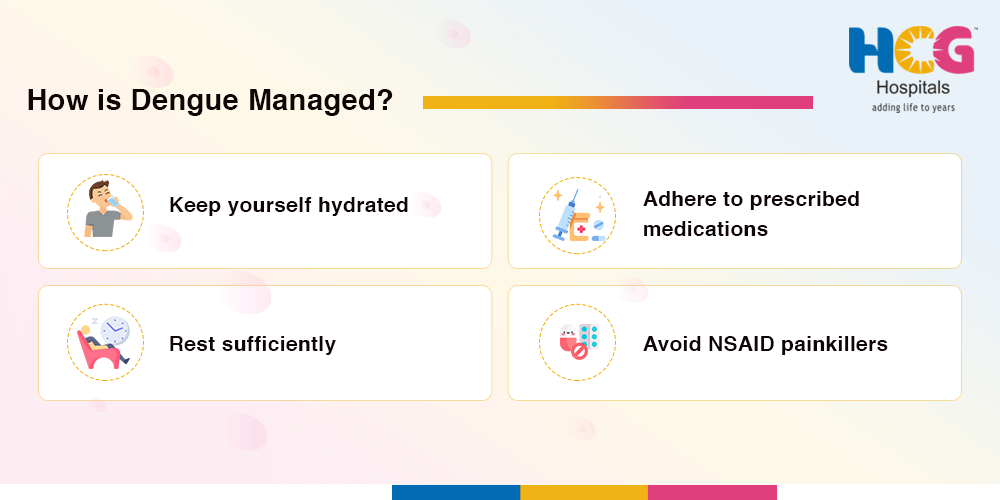
If the patient is diagnosed with dengue, rest and hydration are important. Supportive management with fever-reducing drugs, monitoring severe symptoms, and consulting the doctor are also recommended.
Prevent dengue while travelling by applying mosquito repellent, wearing long-sleeved clothing and long pants, staying in air-conditioned or screened accommodations, avoiding high mosquito activity areas, and eliminating standing water around your stay. Moreover, stay informed about local dengue outbreaks.
A reduced platelet count is a common condition associated with dengue infection. Patients with dengue have a low blood count for several reasons.
First, the virus affects the bone marrow function of producing platelets. Second, there is a high rate of destruction and removal of platelets in the bloodstream. Thirdly, the body’s immune system also produces antibodies during dengue infection, which may lead to a reduced platelet count.
The complications of a reduced platelet count include bleeding, which is one of the most common reasons for morbidity and mortality in patients with dengue.
Patients with dengue have flu-like symptoms that usually last for 2 to 7 days. Patients experience dengue fever after an incubation period of 4 to 10 days after the mosquito bite. Patients may have a high fever (104°F) along with at least two of the following symptoms, i.e., pain behind the eyes, headaches, swollen glands, nausea and vomiting, rash, and joint pain.
In dengue cases, avoid spicy foods that may increase bleeding risks, high-fat and processed foods, and limit caffeine and alcohol.
Diagnosis involves confirmation of the presence of the dengue virus or its antibodies by blood tests. A proper medical evaluation, based on symptoms and laboratory results, is necessary for diagnosis.
Consumption of light and easily digestible foods like soups and fruits, particularly those rich in vitamin C and cooked vegetables, may positively impact the recovery from dengue. Fluid replacement is essential.
The medication for dengue depends on the symptoms and their severity. Doctors may prescribe medicines to lower fever and reduce inflammation.
Dengue fever treatment involves adequate hydration, good nutrition, monitoring for complications, a gradual return to normal activities, and constant medical follow-up.
This will ensure a complete recovery and prevent recurring attacks of dengue fever.